Halal meat is more than just a dietary preference — it’s a religious obligation for Muslims, rooted in deep spiritual and ethical principles. Whether you’re a curious non-Muslim or a new Muslim trying to understand what is halal meat and Islamic dietary laws, this guide breaks it all down in a simple, engaging way.
What Does “Halal” Mean?
Halal is an Arabic term meaning “permissible” or “lawful” in Islam. It applies to all aspects of life but is most commonly used to refer to food and drink that are allowed under Islamic Shariah law.
🕋 The Holy Qur’an Reference:
“He has only forbidden to you dead animals, blood, the flesh of swine, and that which has been dedicated to other than Allah. But whoever is forced [by necessity]… there is no sin upon him.”
➡️ This verse outlines key haram (forbidden) items and makes exceptions only in life-threatening situations, showing Islam’s practicality. Moreover, this is one of the most detailed verses on dietary laws, reinforcing the importance of eating meat that is slaughtered in the name of Allah.
What is Halal Meat?
Halal meat refers to meat from animals that have been:
- Slaughtered according to Islamic guidelines (Zabiha)
- Raised and handled ethically and hygienically
- Free from any forbidden (haram) substances
🕋 Hadith Reference:
“Verily, Allah has prescribed excellence in all things. So when you slaughter, slaughter well…”
(Sahih Muslim, Hadith 1955)
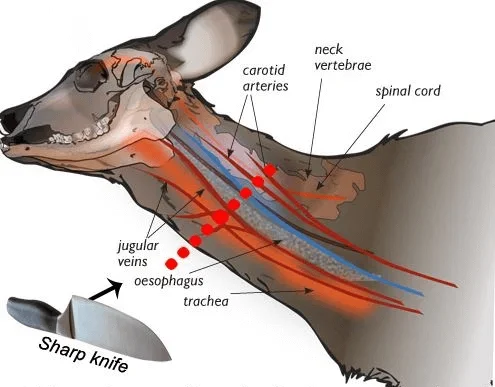
How is Halal Meat Prepared?
The process of preparing halal meat is known as Zabiha and involves the following steps:
✅ Requirements for Halal Slaughter:
- The animal must be healthy at the time of slaughter.
- A Muslim must perform the slaughter while invoking the name of Allah (“Bismillah, Allahu Akbar”).
- The animal’s throat, windpipe, and blood vessels must be swiftly cut to minimize suffering.
- All blood must be drained from the carcass.
- The knife must be sharp to ensure a quick and humane cut.
Difference Between Halal and Non-Halal (Haram) Meat
| Criteria | Halal Meat | Non-Halal (Haram) Meat |
| Slaughtered by a Muslim? | Yes | Not necessarily |
| God’s name invoked? | Yes – “Bismillah, Allahu Akbar” | No |
| Method of slaughter | Zabiha (Islamic method) | Stunning/electric shock/shooting etc. |
| Blood drained completely? | Yes | Often not |
| Animal welfare considered? | Yes – Ethical treatment required | Varies |
| Permissible for Muslims? | Yes | No |
Why is Halal Meat Important to Muslims?
Halal meat is important to Muslims in several following ways;
✨ Spiritual and Ethical Reasons:
- ✅ Halal meat aligns with Islamic teachings and reflects obedience to Allah’s commands.
- 🥩 It ensures the meat is ethically sourced and hygienically prepared.
- 🕋 Animals are slaughtered humanely with the name of Allah invoked during the process.
- 🌱 Promotes compassion, cleanliness, and mindfulness about what is consumed.
- 🙏 Eating halal is a spiritual act that strengthens a Muslim’s faith.
- 🌸 Reinforces the Islamic principle of purity in all aspects of life.
- 🧘 It’s more than just a dietary rule—it’s a symbol of devotion, discipline, and conscious living.
- 📿 Makes halal a vital part of a Muslim’s daily practice and belief system.
🥗 Health Benefits of Eating Halal
- 🩸 Free from Contaminants: Blood is fully drained during halal slaughter, reducing the risk of harmful bacteria and toxins.
- 🧼 Clean and Hygienic: Halal meat comes from healthy animals raised in clean environments.
- 🐑 Ethical and Stress-Free Slaughter: Animals are treated with care, reducing stress hormones like cortisol in the meat.
- 🚫 No Harmful Additives: Halal guidelines prohibit harmful preservatives, antibiotics, and artificial hormones.
- 💪 Nutrient-Rich: Halal meat retains more natural nutrients such as iron, zinc, and essential vitamins.
- 🧘 Supports Mental Well-being: Spiritually clean meat gives consumers peace of mind.
- 🐄 Better Animal Welfare: Humane treatment ensures high-quality, disease-free meat.
Common Misconceptions About Halal Meat
❌ Misconception 1: Halal slaughter is cruel
✅ Truth: Halal requires the animal to be treated with kindness, and the method is designed to minimize pain.
❌ Misconception 2: Halal just means “blessed”
✅ Truth: It’s not just a blessing but a complete set of dietary and ethical laws.
❌ Misconception 3: Any meat sold by Muslims is halal
✅ Truth: Only meat that meets Zabiha standards is truly halal.
Stats and Facts
- In the UK, nearly 20% of all meat sales are halal (Statista, 2023).
- Over 1.9 billion Muslims globally consume halal meat.
- The global halal food market is projected to reach $3 trillion by 2030.
Brief History of Halal Practices
Islamic dietary laws were revealed more than 1,400 years ago. The Prophet Muhammad (ﷺ) emphasized mercy, cleanliness, and moderation in eating.
- Origins in Islam: Halal practices date back to the 7th century, rooted in the Quran and Sunnah, which outline permissible (halal) and forbidden (haram) foods, including meat slaughter methods (*Surah Al-Baqarah 2:173*).
- Medieval Expansion: Islamic empires (Umayyad, Abbasid, Ottoman) standardized halal slaughter (dhabihah) and trade regulations, spreading halal practices across Asia, Africa, and Europe (Ibn Khaldun, Muqaddimah).
- Colonial & Modern Era: Halal certification emerged in the 20th century as Muslim minorities in Europe and the Americas demanded regulated halal meat (Halal Food Authority, UK, 1970s).
- Global Industry: Today, halal is a trillion-dollar market, with strict certification bodies (e.g., JAKIM, ESMA, IFANCA) ensuring compliance (State of the Global Islamic Economy Report, 2023).
Quick Tips to Identify Halal Meat
- Look for certified halal labels from trusted authorities.
- Ask questions about the source and slaughter method.
- Be cautious of terms like “halal-style” — they don’t guarantee Shariah compliance.
What is Halal Meat: FAQs
Final Thoughts
Halal meat is more than just a food choice—it’s a reflection of faith, compassion, and mindfulness. Whether you’re exploring it for religious reasons or ethical ones, understanding what halal meat truly means can lead to more informed and respectful choices.
You may like to know







